Challenges and Solutions in Lateral Guided Boring
Horizontal Drilling, or HDD has appeared as a game-changing technique in the infrastructure and utility installation domains. This cutting-edge method facilitates the installation of pipes, cables, and other infrastructures underground without the necessity for extensive surface disruption. As urban environments become increasingly packed and the requirement for infrastructure grows, understanding how HDD works and its benefits over conventional trenching methods is crucial for engineers, builders, and project managers alike.
Despite its numerous benefits, HDD presents a unique set of challenges that professionals in the industry must overcome. From varying ground conditions to regulatory hurdles, the effective execution of HDD projects demands thorough planning and delivery. In this article, we will examine the main challenges associated with horizontal directional drilling and present effective approaches and responses that can aid minimize these issues, ensuring a favorable outcome.
Summary of Horizontal Directional Drilling
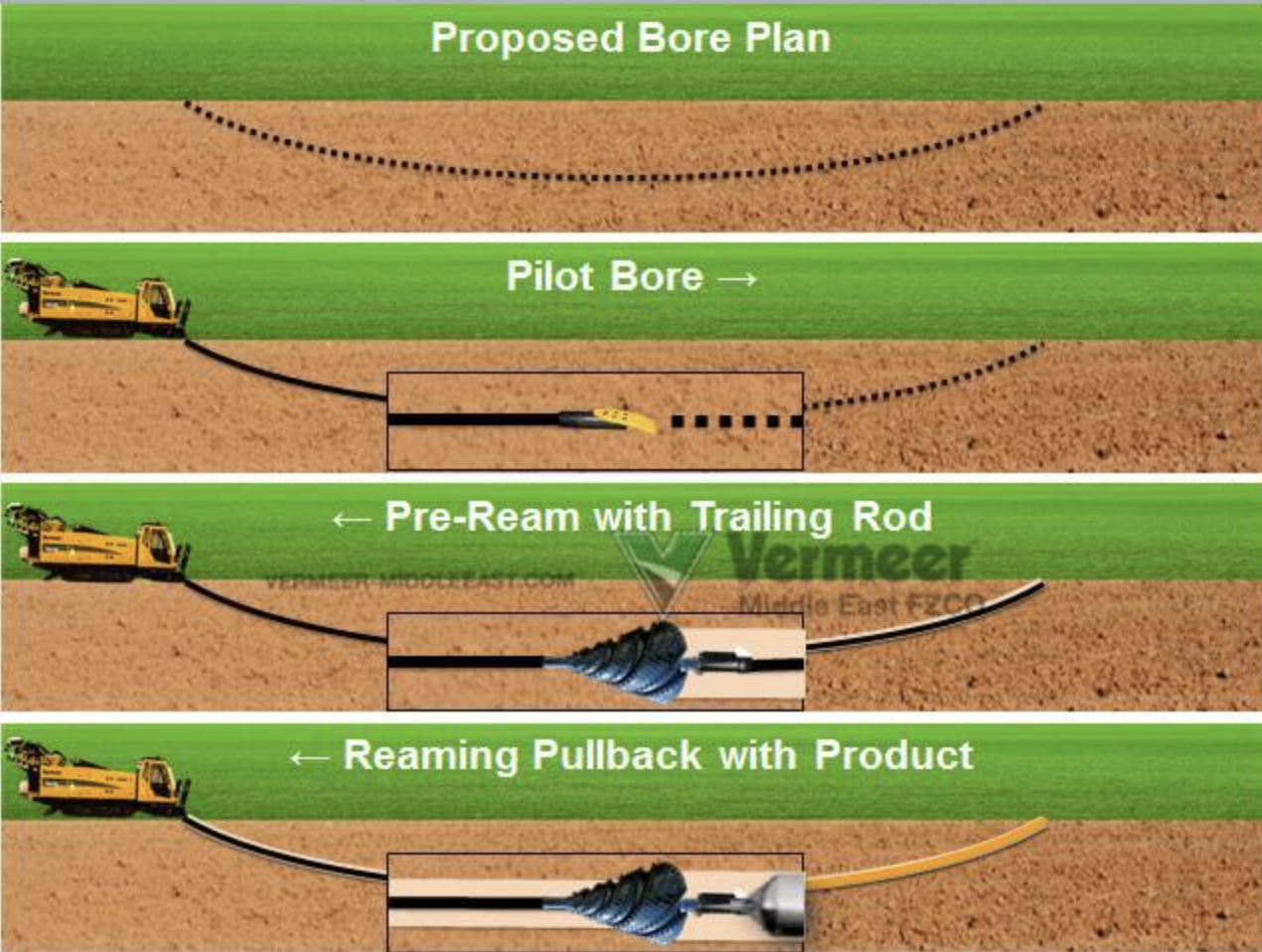
Horizontal Directional Drilling, also known as Horizontal Directional Drilling, is a non-invasive technology used for the installation of subsurface utilities. This method utilizes the use of a boring machine to create a horizontal borehole beneath the ground’s surface, enabling for the placement of tubing, cables, and various infrastructure without the need for extensive digging. The process begins with the drilling of a initial bore, which is then gradually enlarged to fit the utility being installed. By reducing surface disruption, HDD is particularly beneficial in city environments and fragile areas.
The benefits of HDD are notable, particularly when it comes to service installation. In contrast to traditional trenching methods, which can lead to substantial landscape disruption and traffic issues, HDD allows for installation with limited environmental impact. The method is capable of navigating complex landscapes, including rivers and roads, while preserving the integrity of the surrounding area. This makes HDD a favored choice for projects that require a delicate balance between effectiveness and sustainability.
As HDD technology continues to evolve, its applications are expanding across various sectors including communication systems, water and drainage infrastructure, and renewable energy infrastructure. The adoption of advanced technologies such as GPS has improved the accuracy and effectiveness of HDD projects, reducing costs and shortening construction timelines. With an growing emphasis on eco-friendly construction practices, HDD is set to play a crucial role in defining the future of service installation.
Advantages and Uses of HDD
Horizontal Directional Drilling offers many advantages compared to traditional trenching methods, particularly in city environments. One of the key advantages is its ability to reduce surface disruption. Since HDD doesn't need wide trenches, it preserves the integrity of current utilities, roadways, and surroundings, lessening the effects on daily activities and community enterprises. This environmentally friendly method makes HDD an ideal choice for initiatives in densely populated areas where protecting surface integrity is essential.
The uses of HDD go further than utility installation; it plays a critical role in various sectors including telecommunications and sustainable energy. For fiber optic installations, HDD enables for the effective placement of fiber lines without the need for extensive excavation, allowing faster installation timelines. Additionally, for sustainable energy initiatives, HDD is utilized to install buried channels for renewable power systems, ensuring seamless incorporation into the landscape while lessening impact on nature.
Another major advantage of HDD is its adaptability to challenging landscapes. When dealing with complex geologies or crossing bodies of water, HDD offers a dependable solution by drilling horizontally beneath obstacles. This capability not only enhances project feasibility but also substantially reduces the impact on the environment associated with conventional excavation methods. As https://gmaccontractors.com/ for more sustainable construction practices grows, HDD continues to demonstrate its versatility and effectiveness across a wide range of uses.
Obstacles and Effective Strategies in Horizontal Directional Drilling
HDD presents a distinct set of challenges that experts must overcome to ensure successful projects. One significant obstacle is managing soil conditions, as varying soil types can impact drilling performance and tool selection. Difficult substrates, like rock, can hinder progress and increase costs, leading to unexpected delays. To reduce these issues, conducting thorough geotechnical analyses before starting the project is crucial. This allows for the selection of appropriate equipment and techniques customized to the specific soil conditions faced.
Another obstacle involves adhering to permitting and regulatory requirements, especially when operating in urban areas or near fragile environments. Navigating the complex web of local regulations can be time-consuming and may delay project timelines. Best practices include engaging stakeholders early and confirming compliance with all relevant laws. Furthermore, spending time in pre-project planning to develop a comprehensive permitting strategy can streamline the process and minimize disruptions.
Safety is crucial in Horizontal Directional Drilling operations, with risks such as blowouts and inadvertent returns posing potential hazards. Implementing rigorous safety protocols and training for all team members assists to prevent accidents and maintain a safe work environment. Consistently reviewing and updating safety measures based on site conditions and lessons learned from previous projects can enhance safety outcomes. By focusing on these best practices, HDD professionals can successfully overcome obstacles and achieve project success.